Fill in Your Fedex Bill Of Lading Template
Documents used along the form
The FedEx Bill of Lading is a crucial document for shipping, but it often works in conjunction with several other forms and documents. Each of these documents serves a specific purpose in the shipping process, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and complies with regulations. Below is a list of commonly used forms that accompany the Bill of Lading.
- Shipping Invoice: This document outlines the items being shipped, their value, and payment terms. It acts as a request for payment and is essential for accounting purposes.
- Commercial Invoice: Required for international shipments, this invoice details the transaction between the seller and buyer, including product descriptions, quantities, and prices.
- Customs Declaration: This form is necessary for shipments crossing international borders. It provides customs authorities with information about the goods being imported or exported.
- Packing List: A detailed list of the contents of the shipment, including weights and dimensions. This helps in verifying the shipment upon arrival.
- Delivery Receipt: This document is signed by the consignee upon receiving the shipment. It serves as proof of delivery and can be important for resolving disputes.
- Insurance Certificate: If the shipment is insured, this certificate provides proof of coverage in case of loss or damage during transit.
- Hazardous Materials Declaration: Required for shipments containing hazardous materials, this document ensures compliance with safety regulations.
- Freight Release Form: This form allows the carrier to release the freight to the consignee or an authorized agent upon delivery.
- Export License: For certain controlled goods, this document is required to comply with export regulations and must be obtained prior to shipment.
Understanding these documents and their purposes can help streamline the shipping process and reduce potential delays. Always ensure that all necessary forms are completed accurately and submitted on time to avoid complications.
More PDF Templates
Create Pdf Invoice - Promotes timely payments through clear, detailed invoices.
Five Wishes Document - This form fosters trust and communication between you and those responsible for your care.
Similar forms
The FedEx Bill of Lading is similar to a Standard Bill of Lading. Both documents serve as a receipt for the goods being transported. They outline the details of the shipment, including the shipper and consignee information, as well as the nature of the goods. However, the Standard Bill of Lading is typically used for domestic shipments, while the FedEx version is tailored for specific services provided by FedEx Freight. Each document is essential for tracking and verifying shipments throughout the transportation process.
Another document comparable to the FedEx Bill of Lading is the Air Waybill (AWB). An AWB is used primarily for air shipments and acts as a contract between the shipper and the airline. Like the FedEx Bill of Lading, it includes details about the sender, recipient, and contents of the shipment. However, the AWB is non-negotiable, meaning it cannot be transferred to another party, while some Bills of Lading can be negotiable, allowing for transfer of ownership during transit.
The Commercial Invoice is another document that shares similarities with the FedEx Bill of Lading. This invoice is crucial for international shipments, detailing the transaction between the buyer and seller. It includes information about the goods, their value, and the terms of sale. Both documents are necessary for customs clearance, but the Commercial Invoice focuses more on the financial aspects of the transaction, while the Bill of Lading emphasizes the shipping and logistics details.
A Packing List is also akin to the FedEx Bill of Lading. This document itemizes the contents of a shipment, providing detailed descriptions of the items being sent. While the Bill of Lading serves as a contract and receipt, the Packing List is primarily used for inventory management and verification upon delivery. Both documents work together to ensure that the correct items are shipped and received.
The Delivery Receipt is another document that aligns with the FedEx Bill of Lading. This receipt is signed by the consignee upon receiving the shipment, confirming that the goods have been delivered in good condition. While the Bill of Lading is created before shipping, the Delivery Receipt serves as proof of delivery. Both documents are vital for tracking the shipment and resolving any disputes regarding delivery status.
The Freight Bill is similar in that it outlines the charges associated with transporting goods. It includes the cost of shipping, additional fees, and payment terms. While the FedEx Bill of Lading focuses on the shipment's details and conditions, the Freight Bill is centered on the financial transaction. Both documents are essential for accounting and record-keeping purposes.
Lastly, the Customs Declaration is another document that resembles the FedEx Bill of Lading, particularly for international shipments. This declaration provides customs officials with information about the goods being imported or exported, including their value and purpose. Like the Bill of Lading, it is required for customs clearance. However, the Customs Declaration is more focused on regulatory compliance, while the Bill of Lading serves as a contract between the shipper and carrier.
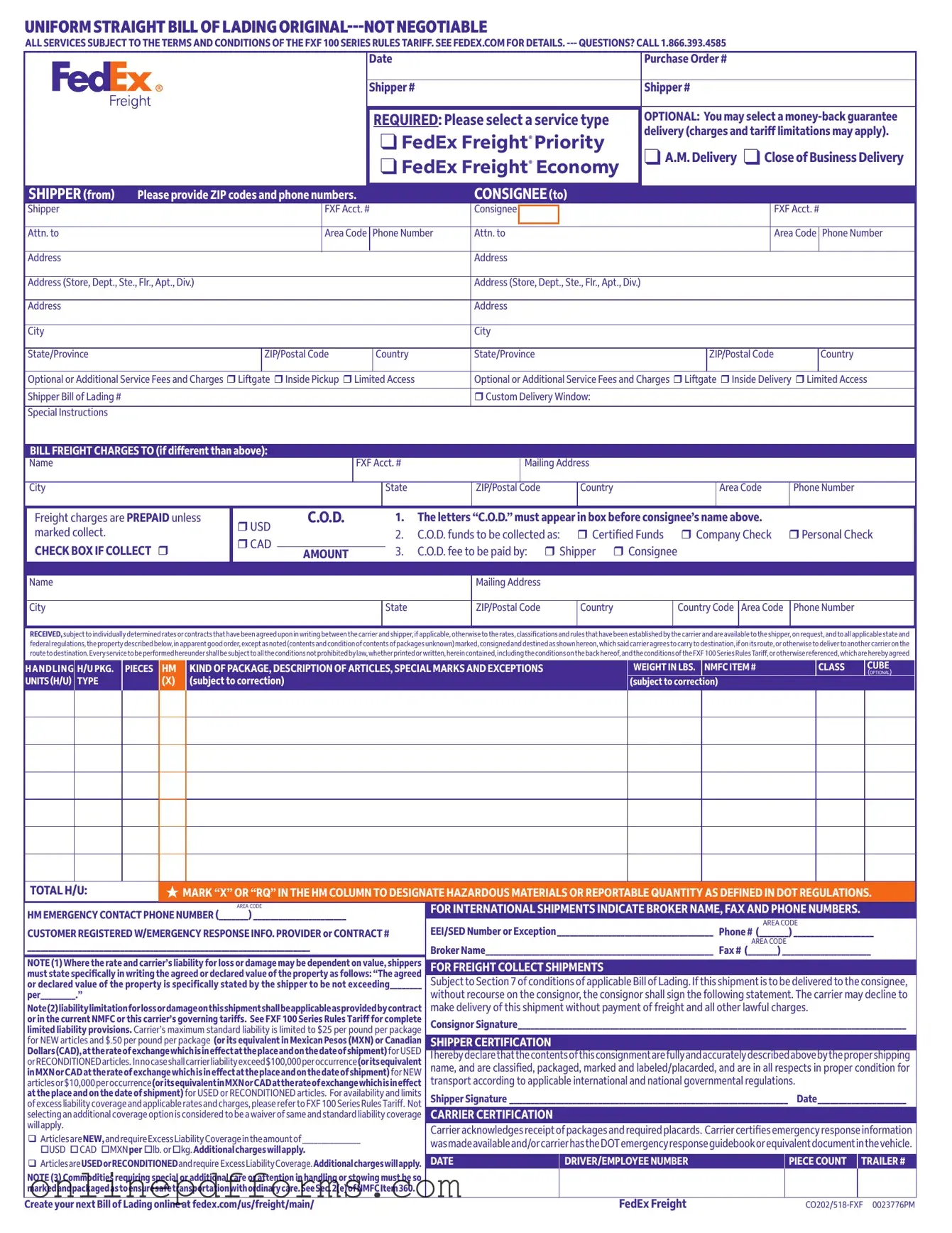
Steps to Filling Out Fedex Bill Of Lading
Filling out the FedEx Bill of Lading form is a straightforward process that ensures your shipment is properly documented. Follow the steps below to complete the form accurately, which will help facilitate a smooth shipping experience.
- Date: Enter the current date in the designated field.
- Purchase Order #: Provide your purchase order number if applicable.
- Shipper Information: Fill in the shipper's details, including the account number, name, address, city, state, ZIP code, and phone number.
- Consignee Information: Enter the consignee’s details, including their account number, name, address, city, state, ZIP code, and phone number.
- Select Service Type: Choose the appropriate service type from the options provided, such as FedEx Freight Priority or Economy.
- Optional Services: Indicate any additional services you may require, like liftgate or inside delivery.
- Freight Charges: Specify who will be responsible for freight charges and indicate if the charges are prepaid or collect.
- C.O.D. Information: If applicable, mark the C.O.D. box and fill in the required details regarding payment methods and amounts.
- Handling Instructions: Describe the handling requirements, including the type and weight of packages, and mark if any materials are hazardous.
- Emergency Contact: Provide emergency contact information, including the broker’s name and phone number if shipping internationally.
- Signatures: The shipper must sign and date the form, certifying that the contents are accurately described and properly packaged.
Once you have completed the form, review it for accuracy before submitting it with your shipment. This will help avoid any delays or issues during transit.