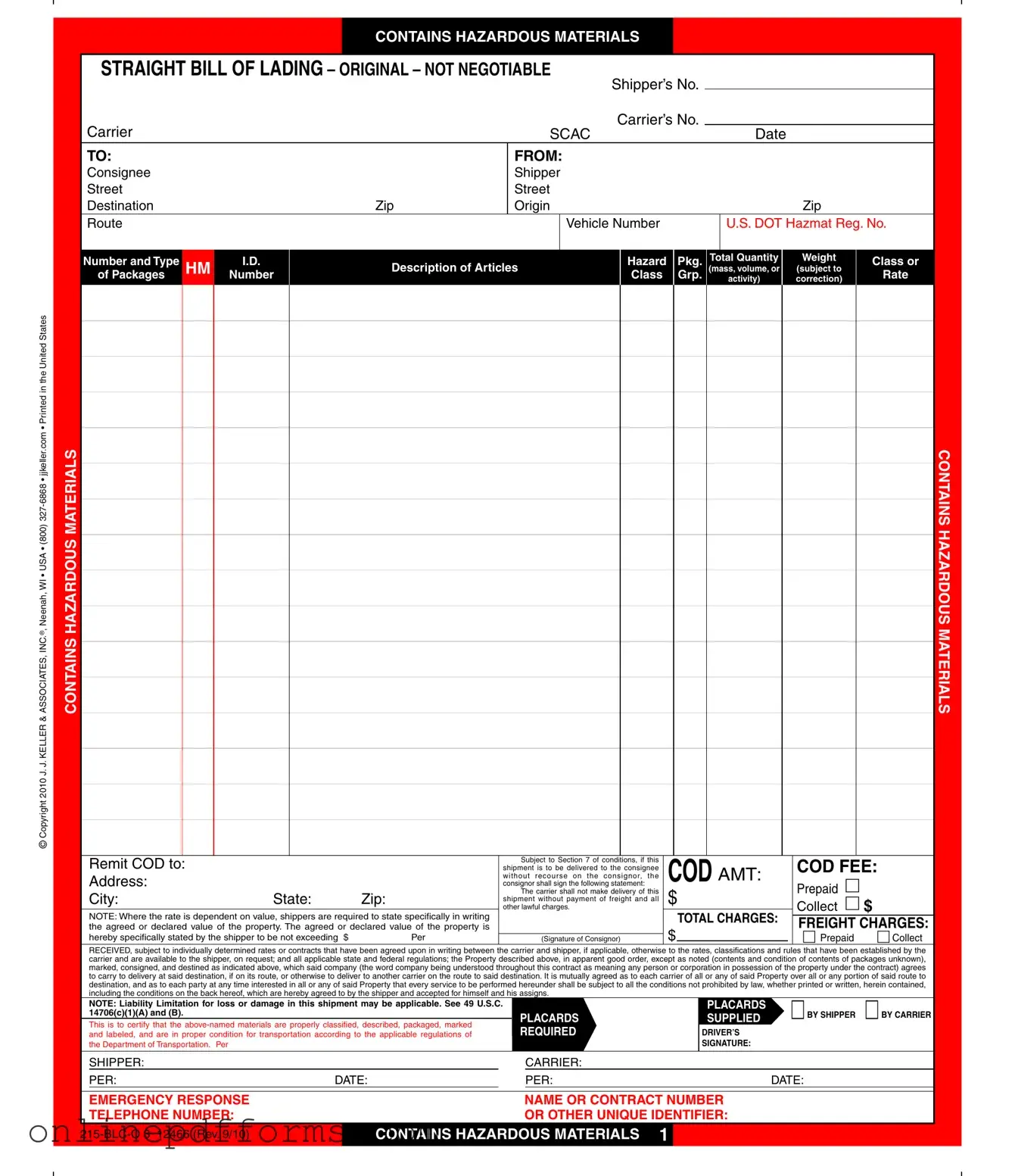
The Hazard Bill of Lading form shares similarities with the Standard Bill of Lading, which serves as a receipt for goods and a contract for their transportation. Both documents outline the responsibilities of the shipper and carrier, detailing shipment specifics such as the type and quantity of goods. However, the Hazard Bill of Lading places a stronger emphasis on hazardous materials, requiring additional certifications and compliance with safety regulations. This ensures that all parties are aware of the risks involved in transporting dangerous goods.
Another document akin to the Hazard Bill of Lading is the Air Waybill. This document is used for air freight and acts as a contract between the shipper and the airline. Similar to the Hazard Bill, it includes shipment details and terms of liability. However, the Air Waybill is typically not negotiable, meaning it cannot be transferred to another party, unlike some forms of the Hazard Bill. Both documents require clear descriptions of the goods, especially when hazardous materials are involved.
The Freight Bill also bears resemblance to the Hazard Bill of Lading. It serves as a receipt for the freight charges and provides evidence of the transportation agreement. While the Hazard Bill focuses on the specifics of hazardous materials, the Freight Bill centers on the financial aspects of the shipment. Both documents require accurate information to ensure compliance and accountability throughout the shipping process.
Additionally, the Delivery Receipt is similar to the Hazard Bill of Lading in that it confirms the receipt of goods by the consignee. This document is often signed upon delivery, providing proof that the goods were received in the condition stated. While the Hazard Bill contains more detailed information about hazardous materials and their handling, the Delivery Receipt serves as a straightforward acknowledgment of receipt.
The Dangerous Goods Declaration is another document that parallels the Hazard Bill of Lading. This declaration is specifically designed for shipments of hazardous materials and outlines the nature of the goods, including any risks associated with their transport. Both documents require detailed descriptions and compliance with safety regulations. However, the Dangerous Goods Declaration is more focused on the specific hazards and necessary precautions, while the Hazard Bill encompasses broader shipping terms.
The Shipping Manifest also shares characteristics with the Hazard Bill of Lading. It lists all items being shipped and is used to verify the contents of a shipment. Both documents require accurate descriptions and quantities of goods. However, the Shipping Manifest is often more comprehensive, detailing multiple shipments under one document, whereas the Hazard Bill focuses on individual shipments, particularly those involving hazardous materials.
The Export Declaration is another relevant document. It provides information on goods being exported from the United States and ensures compliance with export regulations. Similar to the Hazard Bill, it requires accurate descriptions of the goods, especially when hazardous materials are involved. The Export Declaration is essential for customs clearance, while the Hazard Bill primarily governs the transportation process.
The Packing List is akin to the Hazard Bill of Lading in that it provides detailed information about the contents of a shipment. It includes descriptions, quantities, and weights of the items being shipped. While the Hazard Bill serves a broader purpose by establishing terms of transport and liability, the Packing List focuses solely on the inventory of the shipment, making it a useful companion document.
When considering responsible guardianship arrangements, it's important to understand legal documents such as the Power of Attorney for a Child form. This form grants another adult the authority to make decisions for a child, which can be crucial in situations where a parent is unavailable. For those who wish to explore this option further, detailed information can be found at https://arizonaformspdf.com/.
Lastly, the Customs Invoice is similar to the Hazard Bill of Lading in that it provides essential information for international shipments. It includes details such as the value of the goods and their origin, which are crucial for customs clearance. Both documents require accurate and thorough information to ensure compliance with legal requirements, especially when hazardous materials are involved in international transport.